Implement Bellman ford algorithm in java.
Bellman ford algorithm solves the single-source shortest-paths problem in the general case in which edge weights may be negative.
Bellman ford algorithm returns a boolean value indicating whether or not there is a negative-weight cycle that is reachable from the source.
If there is no such cycle,the algorithm produces the shortest paths and their weights.
lets implement Bellman ford algorithm in java,
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BellmanFord
{
private int distances[];
private int numberofvertices;
public static final int MAX_VALUE = 999;
public BellmanFord(int numberofvertices)
{
this.numberofvertices = numberofvertices;
distances = new int[numberofvertices + 1];
}
public void BellmanFordEvaluation(int source, int adjacencymatrix[][])
{
for (int node = 1; node <= numberofvertices; node++)
{
distances[node] = MAX_VALUE;
}
distances[source] = 0;
for (int node = 1; node <= numberofvertices - 1; node++)
{
for (int sourcenode = 1; sourcenode <= numberofvertices; sourcenode++)
{
for (int destinationnode = 1; destinationnode <= numberofvertices; destinationnode++) { if (adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode] != MAX_VALUE) { if (distances[destinationnode] > distances[sourcenode]
+ adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode])
distances[destinationnode] = distances[sourcenode]
+ adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode];
}
}
}
}
for (int sourcenode = 1; sourcenode <= numberofvertices; sourcenode++)
{
for (int destinationnode = 1; destinationnode <= numberofvertices; destinationnode++) { if (adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode] != MAX_VALUE) { if (distances[destinationnode] > distances[sourcenode]
+ adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode])
System.out.println("The Graph contains negative egde cycle");
}
}
}
for (int vertex = 1; vertex <= numberofvertices; vertex++)
{
System.out.println("distance of source " + source + " to "
+ vertex + " is " + distances[vertex]);
}
}
public static void main(String... arg)
{
int numberofvertices = 0;
int source;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of vertices");
numberofvertices = scanner.nextInt();
int adjacencymatrix[][] = new int[numberofvertices + 1][numberofvertices + 1];
System.out.println("Enter the adjacency matrix");
for (int sourcenode = 1; sourcenode <= numberofvertices; sourcenode++)
{
for (int destinationnode = 1; destinationnode <= numberofvertices; destinationnode++)
{
adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode] = scanner.nextInt();
if (sourcenode == destinationnode)
{
adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode] = 0;
continue;
}
if (adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode] == 0)
{
adjacencymatrix[sourcenode][destinationnode] = MAX_VALUE;
}
}
}
System.out.println("Enter the source vertex");
source = scanner.nextInt();
BellmanFord bellmanford = new BellmanFord(numberofvertices);
bellmanford.BellmanFordEvaluation(source, adjacencymatrix);
scanner.close();
}
}
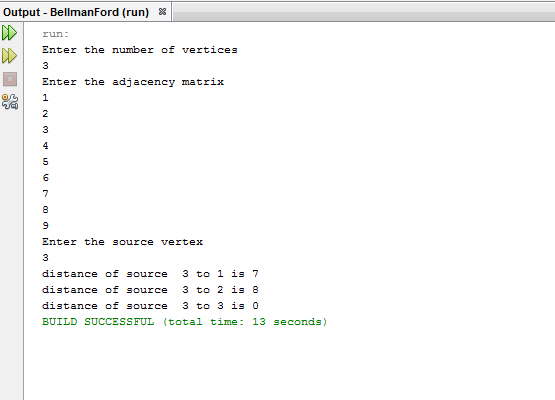
OUTPUT: